Kingdom-Fungi-Agaricus-Yeast | uksir-notes | Diversity-Living-World5
Diversity in Living World 5
 |
| Fungi |
Want to know about Kingdom protista, Click the Link below:
Want to know about Kingdom of classification, Click the Link below:
Kingdom Fungi:
Fungi may be defined as eukaryotic, uni or multi cellular, non green (achlorophyllus) thallus bearing plant, which maintain their life cycle either by Saprophytic/ parasitic/ symbiotic way.
· Study of fungi = mycology
· Father of mycology = P.A. Micheli
· Father of modern Mycology = A. De Bary
· Term Given by = Gaspard Bauhin
General Character:
· Cosmopolitan, mostly terrestrial, few aquatic.
· Vegetative body is called as Thallus.
· The fillamentous body also called as mycelium or hyphae.
· May be saptated or aseptated.
· Cell wall made up of chitin.
· Reserve food is glycogen mostly.
· Mostly heterotrophic- parasitic, saprophytic or symbiotic.
· Symbiotic with the algae group.
· Reproduction takes place by – vegetative , asexual or sexual way.
· Vegetative rep - mostly by fragmentation, fission and budding.
· Asexual rep –by Sporangiospore, zoospore, aplanospore, conidia, binucleated spore etc.
Sexual rep- by Plasmogamy, karyogamy, isogamy, anisogamy, somatogamy, Oogamy, spermatization, gametangial contact, gametangial copulation etc.
 |
| Fungi-Reproduction |
Fungal Classification
There are many Classification system by different Scientists.
One of the common Classification given below: |
| Fungi-Classification |
Class: Phycomycetes (Algal
fungi)
-
Aquatic or found in moist places. (Zygomycetes-
Pin moulds)
-
Aseptated,
Coenocytic mycelium.
-
Commonly
Zoospore production occurs.
-
Sexual
reproduction by Isogamy, Oogamy etc.
-
E.g.: Rhizopus, Mucor, Albugo etc
Class: Ascomycetes:
-
Commonly
known as Sac fungi.
-
Multicellular,
rarely unicellular
-
Saprophytic/
Decomposer, parasitic
-
Asexual
reproduction by conidio spore (conidia)
-
Fruiting
body is called – Ascocarp
-
E.g. : Saccharomyces, Penicillium, Aspergillus,
Neurospora etc.
Class: Basidiomycetes
-
Commonly
called as Club Fungi.
-
Also
called as mushroom group or Puff Ball
-
Mycellium-
branched, septated
-
Commonly
saprophytic, few parasitic.
-
Reproduction
mostly by Asexual spore.
-
E.g.: Agaricus, Puccinia, Ustilago etc.
Class: Deuteromycetes
-
Also
named as fungi imperfecti.
-
Mycellium
Branched and septated.
-
Only
vegetative state is known.
-
Sexual
reproduction not seen.
-
E.g: Altrnaria, Trichoderma, Microsporium etc.
Economic Importance:
Used in:
· Baking/Cake Industry
In medicine industry- Penicilium sp.
· Alcoholic Beverages Industry
· Yeast cake and tablets rich in Proteins and vitamins. As food- Mushrooms.
Some Life History:
RHIZOPUS
Classification:
King- Fungi/ Mycota
Div- Eumycota
ClS- Zygomycetes
Ord- Mucorales
Fam- Mucoraceae
Gen- Rhizopus
Around 10 sp found
Most Common Species- stolonifer
General characters:
· Commonly called- Black mould/ pin mould/ bread mould.
· Saprophytic fungi grow on food.
· Thallus is white cotton like, aseptated and coenocytic hyphae.
· The mycelium may be- long net like called stoloniferous hyphae.
· Which contain root like rhizoids.
Some time grow to sporangiophore to produce spore. |
| Rhizopus |
Life cycle / Reproduction:
· Vegetative reproduction- mostly by fragmentation.
· Asexual Reproduction- sporulation
· Spores are produced on Sporangia/ Sporangiophore.
· Spores very minute, non motile, uninucleated called sporangio spore.
· They spread by wind and again germinate to vegetative mycelium.
· Sexual reproduction- by Gametangial copulation.
 |
| Rhizopus-reproduction |
Agaricus :
 |
| Mushroom |
Classification:
- Kingdom- Fungi
- Division – Eumycota
- Class- Basidiomycetes
- Order- Agaricales
- Family- Agaricaceae
- Genus- Agaricus
General Characters:
· Commonly called as Mushrooms.
· Saprophytic, develop in moist area, with high humus contain.
· Primary Mycellium- Hyaline, Septate , monokaryotic
· It is of + and – Strains.
· They form secondary mycelium by fusion forming a dense structure called Rhizomorphs.
· At maturity they form fruiting body.(Mushroom)
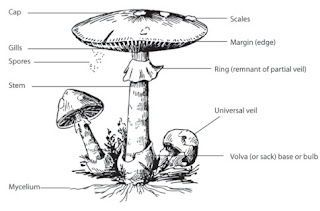
· Fruiting Body- Umbrella shape, Contain Pilus (Cap)and a stalk (stipe)
Pilus contain Gills (300-600) which produce spore.
 |
| Agaricus |
Reproduction:
· Vegetative Reproduction – mostly by Fragmentation.
· Asexual Reproduction – very rare, by Chlamydospores.
Sexual Reproduction - with out sex organ, By Somatogamous fusion. |
| Agaricus-Reproduction |
YEAST/ SACCHAROMYCES
Classification:
- Kingdom- Fungi
- Division – Eumycota
- Class- Hemiascomycetes
- Order- Endomycetales
- Family- Saccromycetaceae
- Genus- Saccharomyces
- Most Common Species- cerevisiae
General Characters:
- Unicellular, Eukaryotic, Saprophytic Fungus.
- Mostly contain- 2 strains (Dwarf strain and Large strain)
- Almost similar except the size.
- Dwarf Strain- Haploid (+/ - strain), spherical cell
Large strain- Diploid (2n), ellipsoidal cell. |
| Yeast |
- Cell wall present, Birth scar may found.
- Reserve food- glycogen and oil globule.
- Central large vacuole present with peripheral nuclei.
- Love to grow in sugar or carbohydrate medium.
- Contain Zymase enzymes, for Fermentation process (Ethyl alcohol)
- Reproduction includes-
Vegetative and sexual reproduction.
Most common process is – Fission and Budding.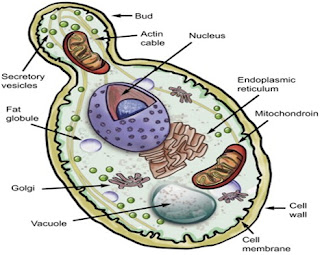 |
| Yeast-Budding |
- Chain of Buds may found looks like pseudo mycellium.
- Sexual Reproduction- mostly by 3 type
- Haplo- diplontic Life Cycle (S. cerevisiae)
- Haplo- biontic Life cycle (S. octosporous)
Diplo- Biontic Life cycle (S. ludwigi)Want to know about Taxonomy- Nomenclature, Click the Link below:
Want to know about Kingdom of classification, Click the Link below:





No comments