NEET-NCERT-SYLLABUS-UKSir
 |
| NCERT |
 |
| Syllabus |
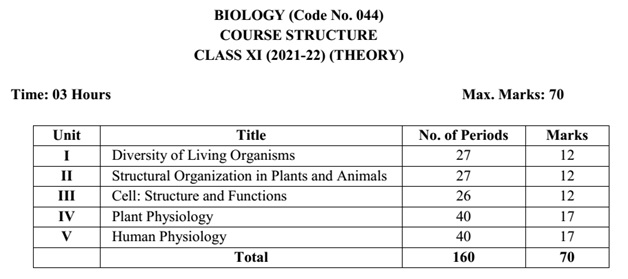
Unit-I Diversity of
Living Organisms
Chapter-1: The Living World
What is living? Biodiversity; Need for classification; taxonomy and systematics; concept of species and taxonomical hierarchy; binomial nomenclature; tools for study of taxonomy museums, zoological parks, herbaria, botanical gardens, keys for identification.
Chapter-2: Biological Classification
Five kingdom classification; Salient features and classification of Monera, Protista and Fungi into major groups; Lichens, Viruses and Viroids.
Chapter-3: Plant Kingdom
Salient features and classification of plants into major groups - Algae, Bryophyte, Pteridophyta, Gymnospermae and Angiosperm (salient and distinguishing features and a few examples of each category): Angiosperms - classification up to class, characteristic features and examples. Plant life cycles and alternation of generations
Chapter-4: Animal Kingdom
Basis of Classification; Salient features and classification of animals, non-chordates up to phyla level and chordates up to class level (salient features and distinguishing features of a few examples of each category). (No live animals or specimen should be displayed in school.)
Unit-II Structural
Organization in Plants and Animals
Chapter-5: Morphology of Flowering Plants
Morphology and modifications: Morphology of different parts of flowering plants: root, stem, leaf, inflorescence, flower, fruit and seed. Description of families: Fabaceae, Salicaceae and Liliaceous (to be dealt along with the relevant experiments of the Practical Syllabus).
Chapter-6: Anatomy of Flowering Plants
Anatomy and functions of different tissues and tissue systems in dicots and monocots. Secondary growth.
Chapter-7: Structural Organization in Animals
Animal tissues; Morphology, Anatomy and functions of different systems (digestive, circulatory, respiratory, nervous and reproductive) of an insect-cockroach (a brief account only).
Unit-III Cell:
Structure and Functions
Chapter-8: Cell-The Unit of Life
Cell theory and cell as the basic unit of life, structure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells; Plant cell and animal cell; cell envelope; cell membrane, cell wall; cell organelles - structure and function; endomembrane system- endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, Golgi bodies, lysosomes, vacuoles; mitochondria, plastids, micro bodies; cytoskeleton, cilia, flagella, centrioles (ultrastructure and function); nucleus.
Chapter-9: Biomolecules
Chemical constituents of living cells: biomolecules, structure and function of proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids; concept of metabolism; Enzymes - properties, enzyme action, factors, classification, Co-factors.
Chapter-10: Cell Cycle and Cell Division
Cell cycle, mitosis, meiosis and their significance
Unit-IV Plant
Physiology
Chapter-11: Transport in Plants
Movement of water, gases and nutrients; cell to cell transport - diffusion, facilitated diffusion, active transport; plant-water relations, imbibition, water potential, osmosis, plasmolysis; long distance transport of water - Absorption, apoplast, symplast, transpiration pull, root pressure and guttation; transpiration, opening and closing of stomata; Uptake and translocation of mineral nutrients - Transport of food, phloem transport, mass flow hypothesis.
Chapter-12: Mineral Nutrition
Elementary idea of hydroponics as a method to study mineral nutrition; essential minerals, macro- and micronutrients and their role; deficiency symptoms; mineral toxicity; nitrogen metabolism, nitrogen cycle, biological nitrogen fixation.
Chapter-13: Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
Photosynthesis as a means of autotrophic nutrition; early experiments, site of photosynthesis, pigments involved in photosynthesis (elementary idea); photochemical and biosynthetic phases of photosynthesis; cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation; chemiosmotic hypothesis; photorespiration; C3 and C4 pathways; factors affecting photosynthesis.
Chapter-14: Cellular Respiration
Exchange of gases; do plants breathe; cellular respiration - glycolysis, fermentation (anaerobic), TCA cycle and electron transport system (aerobic); energy relations - number of ATP molecules generated; amphibolic pathways; respiratory quotient.
Chapter-15: Plant - Growth and Development
Seed germination; characteristics, measurements and phases of plant growth, growth rate; conditions for growth; differentiation, dedifferentiation and redifferentiation; sequence of developmental processes in a plant cell; growth regulators - auxin, gibberellin, cytokinin, ethylene, ABA; seed dormancy; vernalisation; photoperiodism.
Unit-V Human Physiology
Chapter-16: Digestion and Absorption
Alimentary canal and digestive glands, role of digestive enzymes and gastrointestinal hormones; Peristalsis, digestion, absorption and assimilation of proteins, carbohydrates and fats; egestion; nutritional and digestive disorders - indigestion, constipation, vomiting, jaundice, diarrhea.
Chapter-17: Breathing and Exchange of Gases
Introduction to respiratory organs in animals; Respiratory system in humans; mechanism of breathing and its regulation in humans - exchange of gases, transport of gases and regulation of respiration, respiratory volumes; disorders related to respiration - asthma, emphysema, occupational respiratory disorders.
 |
| Syllabus |
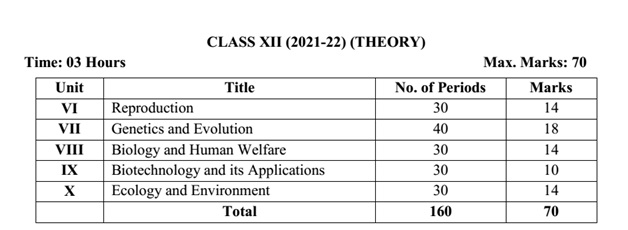
Unit-VI Reproduction
Chapter-1: Reproduction in Organisms
Reproduction, a characteristic feature of all organisms for continuation of species; modes of reproduction - asexual and sexual reproduction; asexual reproduction - binary fission, sporulation, budding, gemmule formation, fragmentation; vegetative propagation in plants; events in sexual reproduction.
Chapter-2: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
Flower structure; development of male and female gametophytes; pollination - types, agencies and examples; outbreeding devices; pollen-pistil interaction; double fertilization; post fertilization events - development of endosperm and embryo, development of seed and formation of fruit; special modes- apomixis, parthenocarpy, polyembryony; Significance of seed dispersal and fruit formation.
Chapter-3: Human Reproduction
Male and female reproductive systems; microscopic anatomy of testis and ovary; gametogenesis - spermatogenesis and oogenesis; menstrual cycle; fertilization, embryo development upto blastocyst formation, implantation; pregnancy and placenta formation (elementary idea); parturition (elementary idea); lactation (elementary idea).
Chapter-4: Reproductive Health
Need for reproductive health and prevention of Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs); birth control - need and methods; medical termination of pregnancy (MTP); amniocentesis; infertility and assisted reproductive technologies - IVF, ZIFT, GIFT, AI (brief overview).
Unit-VII Genetics and
Evolution
Chapter-5: Principles of Inheritance and Variation
Heredity and variation, Mendelian inheritance; deviations from Mendelism – incomplete dominance, co-dominance, multiple alleles and inheritance of blood groups, pleiotropy; elementary idea of polygenic inheritance; chromosome theory of inheritance; chromosomes and genes; linkage and crossing over; Sex determination - in human being, birds, grasshopper and honey bee; Mutation, Pedigree analysis, sex linked inheritance - hemophilia, color blindness; Mendelian disorders in humans –sickle cell anemia, Phenylketonuria, thalassemia; chromosomal disorders in humans; Down's syndrome, Turner's and Klinefelter's syndromes.
Chapter-6: Molecular Basis of Inheritance
Structure of DNA and RNA; DNA packaging; Search for genetic material and DNA as genetic material; DNA replication; Central Dogma; transcription, genetic code, translation; gene expression and regulation - lac operon; Human genome project; DNA fingerprinting.
Chapter-7: Evolution
Origin of life; biological evolution and evidences for biological evolution (paleontology, comparative anatomy, embryology and molecular evidences); adaptive radiation; Biological evolution: Lamarck’s theory of use and disuse of organs, Darwin's theory of evolution; mechanism of evolution - variation (mutation and recombination) and natural selection with examples, types of natural selection; Gene flow and genetic drift; Hardy - Weinberg's principle; brief account of evolution; human evolution.
Unit-VIII Biology and
Human Welfare
Chapter-8: Human Health and Diseases
Pathogens; parasites causing human diseases (malaria, dengue, chikungunya, filariasis, ascariasis, typhoid, pneumonia, common cold, amoebiasis, ring worm) and their control; Basic concepts of immunology - vaccines; cancer, HIV and AIDS; Adolescence - drug and alcohol abuse.
Chapter-9: Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
Animal husbandry, Plant breeding, tissue culture, single cell protein.
Chapter-10: Microbes in Human Welfare
Microbes in food processing, industrial production, Antibiotics; production and judicious use, sewage treatment, energy generation and microbes as bio-control agents and bio-fertilizers.
Unit-IX Biotechnology
and its Applications
Chapter-11: Biotechnology - Principles and Processes
Genetic Engineering (Recombinant DNA Technology).
Chapter-12: Biotechnology and its Application
Application of biotechnology in health and agriculture: genetically modified organisms - Bt crops; RNA interference, Human insulin, gene therapy; molecular diagnosis; transgenic animals; biosafety issues, bio piracy and patents.
Unit-X Ecology and
Environment
Chapter-13: Organisms and Populations
Organisms and environment: Habitat and niche, abiotic factors, ecological adaptations; population interactions - mutualism, competition, predation, parasitism, commensalism; population attributes - growth, birth rate and death rate, age distribution.
Chapter-14: Ecosystem
Ecosystem: structure and function; productivity and decomposition; energy flow; pyramids of number, biomass, energy; nutrient cycles (carbon and phosphorous); ecological succession; ecological services - carbon fixation, pollination, seed dispersal, oxygen release (in brief).
Chapter-15: Biodiversity and Conservation
Biodiversity - Concept, levels, patterns, importance; loss of biodiversity; biodiversity conservation; hotspots, endangered organisms, extinction, Red Data Book, Sacred Groves, biosphere reserves, national parks, wildlife, sanctuaries and Ramsar sites.
Chapter-16: Environmental Issues
Air pollution and its control; water pollution and its control; agrochemicals and their effects; solid waste management; radioactive waste management; greenhouse effect and climate change impact and mitigation; ozone layer depletion; deforestation; case study exemplifying success story addressing environmental issue(s).
*****




No comments