Eukaryotic-Nucleus-chromatin | Notes-by-UK-Sir | Cell-Bio- 14
CELL (Nucleus-chromatin)
Want to Know about Ribosome, Peroxisome, Glyoxysome :
https://uksirnotes.blogspot.com/2021/07/Ribosome-Peroxisosomes-Glyoxysome-uksirnotes.html
Nucleus
• It
is Double membrane bound protoplasmic body with all genetic material.
• Control
room or controlling center of cell.
• Considered
as largest cell organelle.
• Discovered
By Robert Brown 1831
• Present
in all eukaryotic cells – except RBC and sieve cells.
• Size
is – 5 – 25 μm diameters.
• Number – may be Uni nucleated, Bi- Nucleated in Protistans, Multinucleated - fungi , algae, Bone marrow cells latex vessel cells, etc. (in animals multinucleated condition called as- syncytial cell, in plants and fungi- coenocytic cells)
• Position- mostly – central, in Plants and adipocytes (fat store cells)- Peripheral, Glandular cell- basal, suspended in central vacuole by strand– in Spirogyra.
• Shape- generally rounded, Oval or elliptical – in plants , Disc shaped in Squamous epithelium, Lobbed in WBC, Irregular branched- silk spinning cells of insects.
• Composition-
• DNA
(9-12%), RNA (5%), LIPIDS (3%), Basic Proteins (15%), Acid Proteins, neutral
and enzyme proteins (65%) minerals- Ca,
Mg, K, Na etc
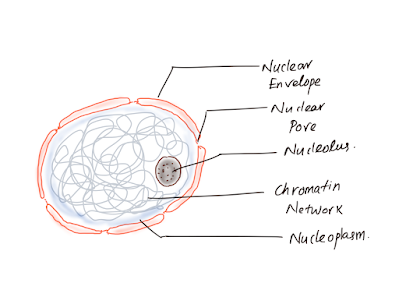
Ultra structure
5 parts-
•
Nuclear envelope
•
Nucleoplasm
•
Nuclear matrix
•
Chromatin
•
Nucleolus
 |
| Nucleus |
A. Nuclear Envelope(Karyotheca)
• Two
membranes present (thickness 60 – 90 A0)
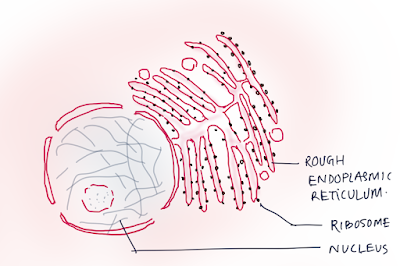
• Outer
membrane - may be smooth or rough (due to Ribosome)
• Inner
membrane is - smooth
• Space
between two membrane, Called as Perinuclear space (100-500 A0)
• Outer
membrane is - connect to ER.
• Envelope
contain- large number of pores (10%)
• Protein
present in pore is – nucleoporins (form annulated pore complex)
• Control
the passage of substances like – RNA, ribosomes, proteins etc.
B.Nucleoplasm (Nuclear sap)
• Semi
fluid, colloidal, transparent, substance present inside Nucleus.
• Just
like Cytoplasmic composition with Nucleic acids, Enzymes, etc.
C. Nuclear Matrix
• It
is Network of fine fibrils of proteins.
• Nucleus
matrix form a dense fibrous layer- nuclear lamina or fibrous lamina.
• 2
type of fibers - Lamina A and Lamina B present.
• Gives
mechanical strength, Attachment for chromatin etc.
D. Chromatin (by Flemming 1879)
• It
is DNA and Protein containing fiber complex.
• Network
of fiber like structure- Chromatin Network/ chromatin reticulum.
• Can
form two type of region-
• Euchromatin
region- narrow part (10-30nm), Light color area.
• Heterochromatin
region- 100 nm thick, wider, dense, dark color area.
• Whole
chromatin not functional - part of euchromatin is functional.
• During
cell division- chromatin condense to form Chromosome.
E. Nucleolus
• Discovered
By Fontana 1781, described by – Wagner 1840.
• Name
was given by – Bowman- 1840.
• It
is Naked round slightly irregular-
present in chromatin at NOR (Nucleolar Organiser Region) area.
• Number
mostly- 1- 4.
• No
covering /membrane present.
• 4
components maintained by calcium to form the structure.
• Amorphous
matrix - homogenous ground substance with protein.
• Granular
portion is- by protein and RNA(2:1)- scattered as grranule of 150-200 A0
thick.
• The
Fibrillar portion – Nucleolonema – is precursor of granules,
• Nucleonema
is formed by Protein and RNA fibrils (
50-80 A0)
• Chromatin
Portion- Perinucleolar (present in periphery) and Internucleolar (inside
the nucleolus as trabiculae).
• Nucleolus
is– Principal site of rRNA synthesis.
Nucleus Function
• Store
Genetic information in the form of Chromatin.
• Chromatin
network (DNA + protein) form chromosome.
• It
control all metabolism and activity of cell.
• Ribosome-
formed at nucleous.
• Control
Cell growth and development, maintenance, cell differentiation, variation, cell replication etc.
https://uksirnotes.blogspot.com/2021/07/Ribosome-Peroxisosomes-Glyoxysome-uksirnotes.html



No comments