Lysosome-cytoskeleton | Notes-by-UK-Sir | Cell-Bio-9
CELL (Lysosome and Cytoskeleton)
Lysosome
•
Discovered
By Christian De Duve in 1955.
•
Term
given by Novikoff in 1956.
•
These
are Small single membrane bound digestive or hydrolytic enzymes containing
structures.
•
Here
Digested food recycled-there for called as Recycling Centre.
•
Also
called Suicide bags.
•
It’s
a small vesicle with semi-crystalline structure of enzymes.
•
About
50enzymes can be found.
•
Enzymes
are acid hydrolases (pH 4-5).
•
Enzyme
contain differ from cell to cell.
•
Most
common are Phosphatases, Protease, Nuclease, lipase etc.
•
Shape mostly Rounded or Irregular (in Root tip
cell).
•
Diameter
is 0.2-0.8 μm
•
Some
time up to 5 μm
in Kidney cells, Leucocytes.
•
The
matrix may be solid or differentiated (inner less dense and outer dense area).
•
Present
in all animal cells but absent in RBC.
•
Abundant
in Phagocytic cells.
•
Formed
jointly by ER and Golgi Body.
•
Hydrolytic
enzymes transferred by RER.
•
Golgian
Vesicle form Lysosome with endosome (Machamer 1993).
•
Lysosomes
Pass through Polymorphism.
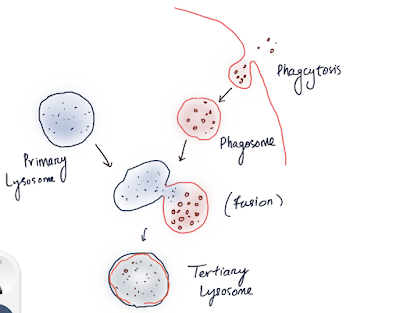
•
Primary Lysosome: these are Newly formed vesicle from Golgi Apparatus.
•
Small,
but contain hydrolytic enzymes in the form of Granules.
•
Secondary Lysosome: these are Hetero Phagosomes or Digestive Vacuoles.
•
Formed
when fused with Phagosome and help in Digestion.
•
Residual Bodies: Tertiary Lysosome.
•
Here
indigested food / left over are present.
•
They
Show Ephagy or Exocytosis.
•
They
cause ageing when not thrown out.
•
Lipofuschin
pigment granules are example residual body.
•
Autophagic Vacuoles (Auto-phagosome/Autolysosome)
•
Fusion
of many lysosome around worn out or degenerated organelles Form autophagy or
auto-digestion.
•
For
which called as Disposal Bag or Disposal Units.
•
Also
perform Autolysis- death of cell.
Function
•
Help
in Intercellular Digestion.
•
Help
in Extracellular digestion.
•
Perform
Body Defense.
•
Help
in Autophagy- for which metamorphosis occurs.
•
Removal
of Obstruction is due to lysosome.
•
These
are involved in Intracellular Scavenging.
•
Sperm
Lysin produced by it - Break the
membrane of egg.
•
Help
in Formation of thyroxin – by hydrolysis of thyroglobulin.
•
Help
in Removal of Carcinogens.
•
Form
Leucocyte granules.
•
Help
in Osteogenesis – during bone formation lysosome help in the process. Thus
cartilage forms bone.
•
Remove
old cell- prevent ageing.
CYTO SKELETON
Definition:
•
It
is the frame work in side cell which maintain the internal Structure of the
cell.
•
Present
only in Eukaryotic cell.
•
Maintain the shape of the cell.
•
These
are minute fiber like tubular network structure.
Structure
Contain 3
Things:
A. Micro filament
B. Intermediate filament
C. Microtubule
A) Micro filament (by Paleviz et al 1974)
•
These
are Long narrow cylindrical rods.
•
Protein
filaments – made by Actins (of 6-8 nm diameters).
•
Globular
actin filaments show beaded helical structure.
•
They
Form hexagonal bundle or parallel bundles.
•
They
are Contractile - connected to Spindle Fiber, ER, Chloroplast etc.
•
In
Intestinal cell microvilli present which contain microfilament.
B) Inter mediate filament
•
Nearly
Solid, unbranched filament structure forms a network like structure.
•
10nm
thick with variety of protein.
•
These
filaments are of 4 type:
•
Keratin
Filaments -present in skin
•
Neuro
filaments-present in axon and dendron of nerve cell.
•
Glial
Filaments- found in astrocytes (Star shape brain cell)
•
Heterogeneous
filament- found in muscle (Z-line and M-line)
C) MICRO TUBULE (by De Robertis and Franchi 1953)
•
These
are Unbranched hollow tubules.
•
The
Protein is- Tubulin (alpha and Beta Tubulin)
•
Common in eukaryotes- cytoplasm, centrioles, basal bodies,
flagella cilia , spindle apparatus, chromosome fiber, sperm tail etc.
•
Can
easily grow and cutoff as monomers(Single units).
•
Indefinite
in length.
•
With
25nm diameter.
•
The
Proto filaments helically
arranged to form large tubules.
•
Lateral
projections may found.
 |
| Cytoskeleton |
Function:
•
Microfilament-
Cytoplasmic streaming, support to cytoplasm, micro fibril formation,
pseudopodia formation, Membrane undulation (wave like) etc.
•
Intermediate filament-
Formation of Nuclear matrix, muscle, keratin of skin, gives
mechanical strength to nerve tissue, membrane, cytoplasm etc.
•
Microtubules-
Formation of Cytoskeleton, Spindle fiber, centriole,
basal body, help in transport, maintain
shape, cell plate formation determined, movement of Chromosome, help in cell
movement etc.





No comments