Cytoplasm-ER-Golgi-complex | Notes-by-UK-Sir | Cell-Bio-8
CELL - Cytoplasm, ER and Golgi Complex
Cytoplasm
• It
is Semi fluid, jelly like substance. (inside Cell membrane)
• Also
Mass of transparent protoplasm with all living characters.
• It
contain cytoplasmic matrix , cell organelles and cell inclusions.
Matrix or Cytosol or Hyalo-plasm
• Can
be found in sol and Gel state and called as Plasma sol and plasma gel.
• Plasma
gel present below membrane i.e. outside- called ectoplast.
• Plasma
sol present inside or at center – endoplast.
• It
is Crystalo-colloidal complex.
• Proteins
form -colloidal particle.
• Water
present up to 90%.
• Inclusions
are – Mineral, sugar, salts, amino acids, t RNA, m RNA, vitamins, enzymes,
ions, excretory material etc.
Function
• Cytoplasm
Contain raw material for survival of cell.
• Matrix
important for cell organelles to hold them in position.
• Help
in Exchange of material by cell organelles.
• It
is the medium for Biosynthesis.
• All
type Metabolism can be seen in cytoplasm.
• Help
in transport of products.
• Eukaryotic
cytoplasm show cytoplasmic streaming or moment
i.e. always in motion (Amici 1818) - it helps in distribution of material all
over the cytosol.
ER (Endoplasic Reticulum)
• Discovered
by Porter and Thompson separately in 1945.
• Name
was given by Porter.
• It
is one network like inter connected membrane channel distributed in 3D
structure.
• It
is part of Endo membrane system of cell.
• It
is Connected with plasma membrane and nuclear membrane.
• Also
connected with adjacent cell ER by plasmodesmata connection.
• Occupy
30-60% of endomembrane system of a cell.
• Can
be divided in to Luminal (inside) and extra Luminal (rest) part.
Structure:
• It
contain Endoplasmic matrix.
• Membranes
are 50-60 A0 thick.
• Contain
3 things-
• 1.
Cisternae: Flat sac like part of 40-50 nm diameters.
• Consists
of Parallel bundles, Finger like projection.
• 2.
Vesicles: oval or rounded structure with 25-500 nm diameters.
• Can
also call as microsomes.
• 3.Tubules:
tube like extensions.
• May
be Irregular or Regular / Branched or unbranched.
• They
have 50-100 nm diameter.
Type:
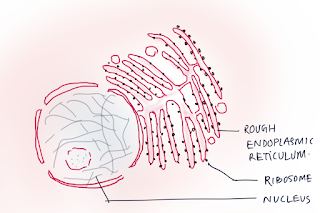 |
| Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum |
1. Smooth ER: (Sarcoplasmic Reticulum)
• No
Ribosome/ With out Ribosome / agranular ER
• Help
in synthesis and storage of- Glycogen, fat, sterols etc.
• Made up of vesicle and tubules.
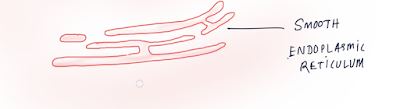 |
| Smooth-Endoplasmic-Reticulum |
2. RER - These are Granular ER due presence of Ribosome.
• 2
type of glycoprotein- Ribophorin 1 and 2 present for attachment of Ribosome.
• Help
in Mostly Protein synthesis and transport.
Function
• Gives
Large surface for physiological activities.
• Gives
mechanical support to Cytoplasmic Matrix and holds the organelles in position.
• Form
plasmodesmata and control inter cellular transport.
• Forms
nuclear envelop.
• It
forms membrane of Golgi body.
• It
forms vacuole.
• Contain
Ribosome for- protein synthesis.
• Contain
different enzymes- (ATpase, reductase, dehydrogenase, phosphatase etc)- for
metabolic activities.
• SER-
Synthesis of fat, sphaerosome, glycogen, sterol, ascorbic acid etc
• Form
Cytochrome P- 450 , 448 which help in Detoxificatoin.
• Release
Ca 2+ -during muscle
contraction.
Golgi apparatus /Golgi Complex / Golgi Body
•
Called
as Golgi Complex/Apparatus/Dalton complex/ Apparato Reticulare.
•
Discovered
By- Camilo Golgi 1898
•
It
is one Complex Cytoplasmic structure mostly present near ER.
•
Made
up of membrane structures- saccules or
cisternae, network of tubule, with vesicle and vacuoles.
Occurrence:
•
Totally
Absent in Prokaryotes.
•
Present
in all Eukaryotic cell ,but absent in
RBC, Sperm of Bryophyte and pteridophyte, sieve tube cell.
•
Present
in Single condition called Localised (in Vertibrates) or in complex / network
like called as diffused (in most invertibrates).
•
In
plant cells- number of unconnected units
found - called as Dictyosomes.
 |
| Golgi-complex |
Structure
•
It
is of Variable shape. Plant dictyosomes are of size– 0.5- 1.0μm.
•
The
Cytoplasm surround to Golgi complex - Zone of Exclusion or Golgi Ground substance.
•
Contain
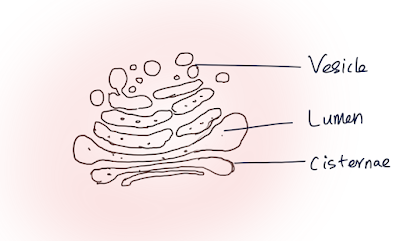
4 parts- Cisternae, Tubules, Vesicles and Vacuoles.
•
Cisternae:
Stacked membrane (3-20) membrane bound.
•
Saccules
or cisternae contain Lumen of 60-90 A0 wide.
•
They
contain parallel fibrils.
•
Cisternae
contain 2 faces-
•
Convex
side/ Cis face or forming face which form Cis Golgi Network- CGN.
•
Concave side/ Trans face or Maturing face
which form TGN. (Trans Golgi Network).
•
Tubules:
Present at maturing face as network.
•
Arise
from Cisternae due to fenestration.
•
Tubules
are interconnected and of 30-50nm diameter.
•
Vesicle: Small
sacs of 20-80nm .
•
Mostly
Attached to the tip of tubules..
•
May
be smooth or coated (rough surface due to protein).
•
Due
to secretory substance called Secretion vesicles
•
Golgian Vacuoles: extended part of cisternae.
•
Develop
from maturing face.
•
Some
time act as lysosome.
Function
•
Help
in Secretion and exocytosis.
•
Transformation
of Membranes.
•
Synthesis
of Glycoprotein and Gyco-lipid.
•
Hormone
production mediated through it.
•
Fat
Transport- fatty acid and glycerol transfer, which are absorbed by intestinal epithelium.
•
Formation
of acrosome i.e. tip of Animal sperm.
•
Vitellogenesis-
In Oocyte of animals, function as center for depostion of yolk.
•
Root
hair formation in Plants.
•
Lysosome
formation also By Golgi Body.
•
Hyponotoxin
- of nematoblasts formed by Golgi Body.
•
Plasmalemma
fromation- from vescisle.
•
New
cellwall formation- middle lamella material and cell wall polysaccharides.





No comments