Eukaryotic-Cell-Ultrastructure | Notes by UK Sir | Cell Bio- 6
Eukaryotic Cell
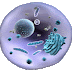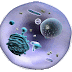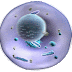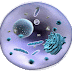
Ultra Structure of plant and Animal cell:
 |
| Plant-animal-cell-difference |
 |
| Plant cell |
Want to know about difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cell, Click the Link below:
Cell wall:
 |
| Cell-wall |
Definition:
• Nonliving , external, Rigid boundary
of Plant cell.
• This is the Supportive and
Protective system of all plant cells .
•
Totally Absent in animals.
 |
| Cell-wall-structure |
Structure:
•
It
is of 3 layers (Middle lamella , primary & Secondary Cell wall)
•
Sometime
Tertiary cell wall may present.
•
Middle
lamella present between adjacent cells.
•
Middle
lamella contain calcium pectate.
•
Primary
cell wall formed during the Early stage of Growth
•
Primary
wall is 1-3 Micrometer thick.
•
In
Primary wall Cellulose contains is maximum.
•
Its elastic & Grow With the cell.
•
Secondary
cell wall formed after Maturation.
•
1mostly
5-10 Micrometer thick.
•
It
is of 3 layered Outer layer, middle layer & inner layer. (S1, S2, S3…)
•
A
tertiary cell wall my formed in few cases according to requirement.
Chemical composition:
following major Constituents
are present:
·
Poly
saccharide. ( Cellulose (10-15%) ,
Hemicellulose (5-15%)&pectin ( 2-8%)
·
Protein 2%
·
Lipid
3%
·
Inorganic
Substances like :(Lignin, Cutin, Suberin, Silica (silicon dioxide), minerals,
wax, tannins, resins, gums etc.)
·
Water (60%)
 |
| Wall composition |
FUNCTION:
• Protection from external Injury.
• Gives particular shape & size.
• Gives mechanical strength to the
cell.
• Permeable to water& Salt.
• Prevent unexpected expansion of the cell.
Plasmodesmata:
 |
| Plasmodesmata |
Structure:
• Cell junctions in plants are called as
Plasmodesmata.
• These are fine cytoplasmic channels
of 20-40 nm diameter.
• At Centre of the channel - narrow
cylindrical Structure - desmotubules present.
• This is the connection of the ER of two adjacent Cells.
Function:
• Passive role in free movement of
metabolites.
• Transport Hormones
• Inter cellular transport of RNA&
Protein mol.
Want to know about Eukaryotic cell property, Click the Link below:
Cell Membrane:
Definition:
All cells are bounded by a membrane surrounding the
cytoplasm called as Cell membrane /Plasma membrane /Plasma lemma .
- It’s a thin, elastic, living & Selectively permeable structure.
- Its dynamic in function and behavior.
Composition:
•
Lipoprotein in nature (lipid- 28-79% , Proteins 20-70%
& Carbohydrates 1-5%)
•
Carbohydrates: Glycoprotein & Glyco lipid
•
Proteins -
 |
| membrane |
• Structural protein form back bone of membrane.
• Lipids have Hydrophobic tail & Hydrophilic head.
There are many Models or Theories have been put forwarded:
1. (Trilaminar)Sandwich model /Lamellar model or Danielli - Davson Model.
-
Proposed by James Danielli & Hugh Davson
(1935)
- Lipid bilayer is covered by – alpha proteins.
- Proteins associate with the polar head of the lipids.
- The layers held together by electro static forces.
- Two type of lipids - Tangentially arranged contact with lipid & another
Globular protein.
 |
| Trilaminar |
2. Unit Membrane model /Robertson model.
 |
| Unit |
- Proposed by J. David Robertson (1959)
- He modified the previous model
- The lipid bilayer is covered in two surface by β-proteins.
- Looks like dense bands separated by a clear zone.
- Dense band is made by up of protein & clear zone is made by lipid.
3. fluid- Mosaic Model :
- Proposed by Singer & Nicolson (1972)
- Lipid & integral proteins are arranged in mosaic manner.
- A continuous layer of Lipid bilayer of
phospholipid embedded with globular proteins.
Membrane lipids are amphipathic in nature. 3 major classes of lipids are present- phospholipid , Sphingolipids (Glycolipid)
& Sterols.
- Lipid bilayer present at center. Lipid molecules have Hydrophilic head & Hydro phobic tail.
- Lipid bilayer show-dynamic motional properties- flexing, lateral diffusion and rotational movement.
- Proteins - 3types of classes. (Structural, enzymes& carrier proteins.)
The integral proteins are tightly attached to hydrophobic core of lipid bilayer.
• Some proteins transverse the membrane to form channel.
• The plasma membrane protein - Intrinsic or Integral and Extrinsic or Peripheral protein. (Globular proteins)
- integral protein is incorporated with hydrophilic polar head.
- The integral protein show diffusion.
Carbohydrates: Glycoprotein & Glyco lipid
 |
| Fluid-mosaic-model |
Function:
- Act as a barrier.
- Compartmentalization in eukaryotic cells.
- Regulate the movement of nutrient molecule & waste material.
- Protect various Organelles.
- Give particular shape.
- Gives elasticity to the cell.
- Contain receptors for signaling.
- In Bacterial membrane- Electron transport chain is present.
- The flip flop movement helps in diffusion.
- Glycolipid helps in cell recognition.
- Transport proteins are specific for transformation process.
Want to know about Eukaryotic cell property, Click the Link below:





No comments