Prokaryotic-Bacteria-Cell | Notes by UKSir | Cell Bio- 3
PROKARYOIC CELL / Bacteria
PROKARYOIC CELL / Bacteria
Prokaryotic-Bacteria
Definition:
•
Bacteria may be
defined as submicroscopic, prokaryotic, cell wall containing, omnipresent
organism, mostly maintain their life cycle either as Saprophytic or as
Parasitic or even as Symbiotic organism.
•
These are mostly
Non-green structure, but Cyanobacteria are green.
•
Can multiply rapidly
and can multiply approximately in ~ 20 mins.
Want to Know about Cell, click link below :
https://uksirnotes.blogspot.com/2021/05/cell-introduction.html
Want to know about Prokaryotic cell properties, Click link below:
https://uksirnotes.blogspot.com/2021/05/difference-prokaryotic-eukaryotic-cell.html
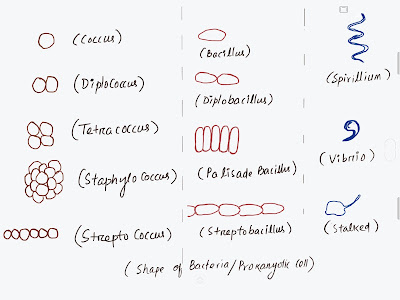
Shape or Form:
1 Coccus-Spherical or Ovoid shape
- Mono coccus- Present Single
- Diplo
coccus- 2 cell present
- Tetra
coccus- 4 cell attached
- Strepto coccus- in chain shape
- Staphylo coccus- irregular shape
- Sarcina coccus- 3D structure
 |
| Bacterial-cell-type |
2.
Bacillus-
Small rod shape or elongated shape
- Diplobacillus (Two cells attached)
- Palisade bacillus (cells are Stack together)
- Strepto Bacillus (cells are in chain)
3. Spirillum- Spirally coiled e.g – spirillium, spiriochaete
4.
Vibrio- Comma
shaped eg-Vibrio cholera
5.
Stalked-
Having a stalk eg- Caulobacter
6.
Budding-
having many out growths. eg – Rhodomicrobium
 |
| Bacteria-Falagella |
1.
Flagellated-
with flagella
- Atrichous- No
flagella
- Monotrichous- single flagella
- Amphitrichous- both end contain flagella
- Lophotrichous- tuft of flagella present at one end
- Cephalotrichous- tuft of flagella present at both end
- Peritrichous-flagella all over the surface
Type of Bacterial cell :on the Basis of stain
•
Gram’s Staining was developed by Christian Gram in 1884
STEPS
INVOVED IN THIS PROCESS:
Ø Bacterial mass - Stain with alkaline
crystal violet
Ø After 30 to 60 sec they looks blue
Ø 0.5% iodine sol is added drop wise
Ø wash with distilled water
Ø absolute alcohol or acetone is added for
few seconds
Ø stain with safranin
Ø Wash with distilled water
Ø Observe under microscope
 |
| Gram-staining-procedure |
Result
•
If
Blue or Violet or purple Colour = Gram +ve Bacteria
(Example - Bacillus
subtilis)
•
If
Colour is Pink / Red = Gram –ve Bacteria
(Example - E.coli)
Reason of color difference:
Ø Gram -ve bacteria : contain High
lipid in cell wall,
which dissolve in Organic solvent like Acetone.
Due to which Gram –ve bacteria become colorless
And looks Pink or Red after adding
of Safranin.
Ø Gram +ve Bacteria: contain less lipid
In cellwall,
for which less color wash out. When safranin added,
they looks either Violet or Purple color.
Want to Know about Cell, click link below :
https://uksirnotes.blogspot.com/2021/05/cell-introduction.html
Want to know about Prokaryotic cell properties, Click link below:
https://uksirnotes.blogspot.com/2021/05/difference-prokaryotic-eukaryotic-cell.html



Thank you sir
ReplyDeleteYou always wel come, happy to help learners.. feel free for any doubts..
DeleteThank you sir it is very help full for me .......
ReplyDeleteits my pleasure.. Be free to ask doubts.
Delete