Plant Physiology-Mineral-nutrition-plants | part - 1 by UK Sir
Mineral Nutrition:-
-
The
process of utilizing raw material by organism to maintain their growth and body
structure is called as Nutrition.
Or
-
The
organic process of nourishing or nourishment is called as Nutrition.
-
When
we study absorption and metabolism of inorganic nutrient, it is called as
Mineral nutrition.
-
Sachs
(1860) and Knops (1865) started a series of experiments.
-
Arnon
and Hoagland (1940) explain about all mineral nutrients.
If You want to know about Respiration, Click the Link below :
https://uksirnotes.blogspot.com/2021/05/plant-physiology-respiration-by-uk-sir.html
If You want to know about Phytohormone , Click the Link below :
https://uksirnotes.blogspot.com/2021/05/phyto-hormones-by-uk-sir.html
Techniques of the Experiments:
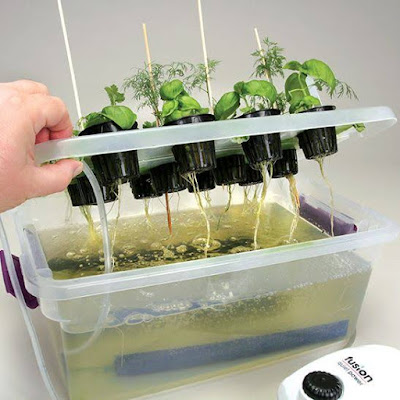 |
| Hydroponics |
-
Technique
for growing plant without soil.
-
Minerals
provided by nutrients solution.
-
Also
aeration is done for root system.
-
It
can be done by 2 methods:
Tank System:
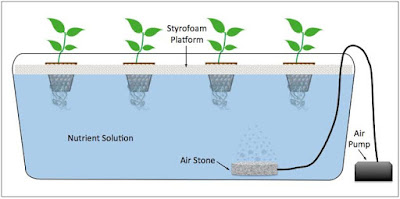 |
| Tank-hydroponics |
-
Here
root of plants are placed in a tank containing nutrients solution.
Film system:
 |
| Film-hydroponics |
-
Here
plants are grown in tubes.
-
A
thin film of nutrient solution is circulated by pumping system.
-
Technique
for growing plant without soil.
-
Here
air or mist environment is used.
 |
| Aeroponics |
-
Mist
is a thin layer of condensed vapor/ fog created by spraying technique.
-
Here
large tank contain liquid solution, with all nutrients.
-
Root
of plants is placed in hanging condition.
-
At
base a motor run rotor to generate mist or moisture cloud.
Inorganic Nutrients:
-
When
nutrients taken/ absorbed in their elemental/ ionic form, it is called
inorganic nutrient.
-
It
includes water and mineral ions.
Classification
-
Grouped
in to two categories:
-
Essential
: ( 17 ) C, H, O, N, P, K, Ca, Mg, S, Fe, B, Mn, Cu, Zn, Mo, Cl and Ni (Al, Si
(Silicon), Na, Ga (Gallium), may be essential for some plant)
-
Non-essential
– all other excluding these are nonessential.
Essential Elements:
-
Term
was proposed by Arnon and Stout (1939)
Some
criteria/ condition to be on essential element:
-
Must
be Essential for normal growth and reproduction, without which plant can’t
complete its life cycle.
-
It
should be specific in requirement, i.e. can’t replace by any other element.
-
Must
involve directly in metabolism.
-
Occurrence
of disorder or malfunction due to its absence.
Based on
required quantity Essential elements can be differentiated in to 2 categories.
i. Macro
elements and ii. Micro Elements
i) Macro elements:
-
Also
called as macronutrients or major elements.
-
They
require to plant in large amount.
-
The
quantity is around 1-10 mg /g dry weight of the plant..
-
Involved
in synthesis of protoplasm and maintaining osmotic potential.
-
C,
H, O, N, P, Ca, K, S, Mg – 9 macronutrients.
-
3
macronutrients are generally deficit in soil called as Critical elements (N, P
& K)
-
So
the fertilizers, with critical elements are called complete fertilizer.
ii) Micro elements:
-
Also
called as Micronutrients or Trace elements.
-
They
required in trace/ less amount by plants.
-
Amount
may be equal or less than 1 mg/g dry weight of the plant.
-
Main
function is enzyme activation, i.e. act as cofactor or metal activator.
-
Zn,
Mn, B, Cu, Fe, Ni, Mo, Cl- 8
microelements.
-
They
become toxic to plant in high conc.
Essential elements – Function and deficiency symptoms:
-
Every
essential element has specific functions.
-
They
are necessary for several vital functions.
- They must maintain their specific conc. Or the plant can’t grow properly.
-
Critical conc.–
the conc. Of essential element below which growth of plant is retarded.
-
Deficiency symptoms:- the morphological changes that indicate deficiency of an element.
Function and deficiency :
i) Macro Elements :
1.NITROGEN (N):
-
Absorbed
in the form of Nitrate, nitrite and ammonia form.
-
Function:
-
Form
protein, nucleic acids, co enzyme, hormones vitamins etc.
-
Helpful
in cell division, growth and photosynthesis.
- Deficiency Disorder
 |
| Chlorosis |
-
like Chlorosis,
dormancy of lateral bud occurs.
-
Premature
leaf fall, delay of flowering may be seen.
-
Stem
may become purple.
2.Phosphorus (P):
-
Can
be absorbed in the form of H2PO4- and PO43-.
-
Function:
-
Form
N.A., protein, ATP, NADP etc.
-
Help
in energy transfer.
-
Form
phospholipid.
Deficiency Disorder :
 |
| Spot-necrosis |
-
Premature
leaf fall, delay of flowering, necrosis, Reduced growth etc.
-
Vascular
tissue poorly developed.
-
Leaf
pigmented (purple and red spot) due to anthocyanin.
 |
| Purple-pigment |
3.Sulphur (S):
-
Absorbed
as SO42- and SO2 from air.
-
Function:
-
Form
vitamins, proteins, Amino acids etc.
-
Help
in chlorophyll formation.
-
Help
in nodule formation.
-
Component
of allylsulphide (of onion, ginger) and sinigrin (of mustard)
-
Deficiency Disorder
-
Chlorosis,
accumulation of anthocyanin.
-
Necrosis,
premature leaf fall, leaf curl.
-
Hard
and woody stem formation.
-
In citrus fruit juice reduction.
Disease caused - Tea yellow.
 |
| Yellow-tea-disease |
4.Calcium (Ca):
-
Absorbed
as Ca2+
-
Function:
-
Help
in maintaining cell permeability.
-
Component
of middle lamella and cell wall.
-
Stabilize
structure of chromosome.
-
Help
in development of root and shoot apex.
-
Organization
of cell wall and mitotic spindle during cell division.
-
Detoxification-
Oxalic acid to calcium oxalate.
-
Deficiency Disorder
 |
| Stunt-growth |
-
Chlorosis
at margin of young leaf.
-
Stunted
growth in plants.
-
Necrosis
can be seen, death of root tip.
-
Premature
fall of flower.
Disease- blossoms rot in Tomato.
 |
| Blossoms-end-rot-tomato |
5.Magnesium (Mg):
-
Absorbed
in the form of Mg2+.
-
Function:
-
Necessary
for synthesis of DNA and RNA .
-
It’s
a component of Chlorophyll.
-
Help
in activation of enzymes.
- Deficiency Disorder
 |
| Inter-vein-chlorosis |
-
Premature
leaf abscission.
-
Leaf
tip curls.
-
Inter vein chlorosis can be seen.
-
Purple
pigmentation can be seen.
-
Formation
of necrotic spot.
 |
| Marginal-necrosis |
6.Potassium (K) :
-
Absorbed
in K+ form.
-
Function:
-
Essential
for Photosynthesis, respiration, protein synthesis etc.
-
Helps
in translocation of food.
-
Help
in stomatal opening and closing.
-
It
act as cofactor of around 40 enzymes.
-
It
maintain turgidity of cell and ion balance.
-
Deficiency Disorder
 |
| leaf-scorch |
-
Apical
bud growth reduced, leads to rosette of bushy habit.
-
Short
internodes founds with loss of cambium activity.
-
Scorching
of leaf can be seen.
Inhibits protein synthesis.
 |
| Rosette-habitat |
Micro elements will be discussed in next part.
If You want to know about Respiration, Click the Link below :
https://uksirnotes.blogspot.com/2021/05/plant-physiology-respiration-by-uk-sir.html
If You want to know about Phyto hormones , Click the Link below :
https://uksirnotes.blogspot.com/2021/05/phyto-hormones-by-uk-sir.html





No comments