Plant Physiology-Photosynthesis-process | by UK Sir
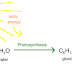
Photosynthesis
The process in which
carbohydrate type of food material is formed by using Carbon dioxide and water
in the presence of chlorophyll pigment & sunlight is called as photosynthesis.
or
The process performed
by green plants for food synthesis is called as photosynthesis.
-The organism perform
photo synthesis are called as photo autotrophs.
 |
| Photosynthesis process |
Want to Know about Cellular Respiration:
https://uksirnotes.blogspot.com/2021/05/plant-physiology-respiration-by-uk-sir.html
Want to Know about Phyto Hormones:
HISTORY:
- Van Helmont (1648) increase in plant substance is due to water.- Stephen Hales: (1727) father of plant physiology - green plants require sunlight.
- Priestley (1772) plant can survive and restore air by burning of candle
- Nicolas T. de Saussure (1804) Total weight of organic matter produced is the by raw material fixed Air and water.
- Palletier & caventou (1818) - discovered and named chlorophyll pigment.
- Von Mayer (1845) - green plant transfer light
energy into chemical energy,
 |
| Photosynthesis site |
- Present in mesophyll cell of the green plants.
- It's a double membrane bound semiautonomous cell organelle.
- Membrane system form- thylakoids & grana.
- Pigments mostly present in grana region.
1.Chlorophyll: –
- Green pigment, convert solar energy to
chemical energy.
- Molecular structure- porphyrin head ( 4 pyrrol
ring with one central Mg atom.)
& a phytol tail ( hydrocarbon tail)
 |
| Chlorophyll -a and b |
- Types - chlorophyll = a, b, c, d, e ( bacterial chlorophyll a & b.)
Chlorophyll- a: ( C55 H 72
05 N4 Mg )
They
are bluish-green in colour, primary photosynthetic pigment, here methyl group
bounded to porphyrin.
Chlorophyll-b:( C55 H 70
06 N4 Mg )
These are Olive green color, accessory pigment, here aldehyde group
present in place of methyl group.
- both Chl- a & b soluble in organic solvent
like alcohol, acetone etc.
2.
Carotenoids.:
( yellow, brown, orange color )
- They prevent photo oxidation and also called
as lipochrome. (fat soluble)
- They act as accessory pigment.
They are of 2 type:
- Carotene: only made up of hydro carbons, C40
H 56,Mostly Orange colour,
e.g- lycopene of tomato. Beta- carotene of carrot.
- Xanthophylls - Yellow colour pigment, here 2
additional oxygen C40 H56 O2 present. Ex-
Lutein, Zeaxanthin.
3. Phycobillins- These are Proteinaceous pigments, red and blue color. Found in BGA and Red algae. Soluble in hot water. Ex- Phycocyanin, phycoerythrin
- Pigments can only absorb at the visible part of light wavelength ( PAR- photosynthetically active region) VIBGYOR.
- Chlorophylls mostly absorb at - 400-500, 700 nm wavelength
- Carotenoids at- 500 nm, and Phycocyanin at - 600 nm
ACTION SPECTRUM
 |
| absorption-and-action-spectrum |
- It’s a graph showing rate of photosynthesis against different wavelength of light.
However Number of Oxygen molecule produced, is considered as rate of photosynthesis.
Emerson’seffect and Red drop :
 |
| Emerson effect red drop |
- Emerson (1957) – more than 680 nm light cause photosynthesis rate reduction called- Red drop.
- But when two wavelength of light use alternatively, It cause photosynthetic rate increase- called as- Emerson’senhancement effect.
Pigment System/ Photosystem :( Photosynthetic Unit)
- Photosynthetic unit - minimum number of pigment require for photosynthetic light reaction.- Thylakoid membrane contain Quantasome (or Photosynthetic units)
- Each Photosystem (LHC) contain - Chlorophylls, carotenoids, proteins etc.
 |
| Pigment-system |
Two Types of PS present-
PS- 1 : Reaction center is P700, present in outer surface of thylakoid, involved in both cyclic and non cyclic photophosphorylation.
PS- 2: Reaction center is P 680. at inner surface of thylakoid membrane, involved in non cyclic photophosphorylation.
Quantum Required – The number of Photon or Quantum require to release 1
molecule of Oxygen by a plant during photosynthesis. (Mostly 8)
QuantumYield – The number of
Oxygen molecule released per photon of light during photosynthesis.
Compensation Point: Rate of Photosynthesis is equivalent to rate of Respiration.
Mechanism ofPhotosynthesis: (Process)
- It’s a Oxidation reduction process. (Water Oxidized, CO2 reduced)- Contain Two Phase:
1) Photochemical phage (Light reaction) 2) Bio synthetic phage (Dark reaction)
 |
| Photosynthesis-process |
1) Light Reaction:
-It’s a light dependent reaction.
-Takes place inside grana thylakoid membrane.
-It starts with absorption of light energy by PS.
- Antenna molecules transfer energy to reaction
center.
-Photolysis of water occurs in to H+,
e- and Oxygen.
-Photolysis of water occurs near PS-II with the
help of MN2+, Cl- and Ca2+
-Here evolution of O2 occurs.
-This Oxygen evolution process also named as
Hill reaction (by R.Hill 1937)
Photophosphorylation :
-Here transfer of electron from PS through an ETS occurs.-It leads to formation of ATP and NADPH2 by using light energy.
-Non Cyclic and Cyclic photophosphorylation.
NON CYCLIC photophosphorylation
 |
| Non-Cyclic-photophosphorylation |
Also called Z -Scheme
-Here ATP formation coupled with non cyclic
transfer of electron (produced from photolysis of water).
- The electrons transfers through a series of
carriers and at last reduce NADP+ to NADPH2
- Transfer of Electron occurs from -
- Here ATP production occurs by pumping of proton ion by Cytochrome complex.
- Here both ATP and NADPH2 produced.
CYCLIC photophosphorylation
 |
| Cyclic-photophosphorylation |
- Here production of
ATP occurs by a cyclic flow of electron.
- Here e- donor and final acceptor is
same.
- In absence of the final acceptor NADP+,
the e- bounce back to ETS.
- From PS-I it again transfer to Fd and
Cytochrome complex.
- Here only ATP is produced.
- It do not involve Photolysis of water.
Product From light reaction
- ATP + NADPH2 (assimilatory power) and O2
-
It
was proposed by P. Mitchell (1961).
-
Here
both Osmotic and Chemical gradient is used for production of ATP
-
Due
to proton pumping, A proton gradient develops across the thylakoid membrane.
-
H+pump from outer side to inner lumen in Chloroplast.
-
But
proton can’t pass through the membrane as it is impermeable.
-
Again
Those H+ move through the F0-F1 particle for maintain the equilibrium.
 |
| Chemiosmotic-Hypothesis |
 |
| Chemiosmotic-Hypothesis |
2) Dark reaction:
- Carbon dioxide reduced to form carbohydrate.
- Also called as Black man's Reaction. (by -Blackman 1905)
- Also called C3 Pathway or Calvin cycle.
- Contain 3 stages:
- ( Carboxylations of RuBp , reduction of CO2 & regeneration of RuBP.)
 |
| Calvin-Cycle |
Carboxylation:
- Atmospheric CO2 fixed to a stable organic compound.- 1st acceptor of carbon dioxide is RuBP.
- With the help of an enzyme RuBisCO.
- This enzyme has affinity towards both O2 & CO2
- It form 2 molecule of phosphoglyceric acid (PGA)
-
Here
formation of glucose occurs by a series of reactions.
-
Here
ATP and NADPH2 utilized to
produce glucose molecule.
-
Here
again RuBp regenerate.
-
Regeneration
of RuBP is essential for CO2 acceptance.
Here utilization of ATP seen to produce 5C Ribulose 1,5- Bisphosphate.
 |
| calvin_cycle_chart |
EndProduct of C3 Cycle:
-
6
Calvin cycle need = for 1 Glucose molecule.
-
For
1 Glucose molecule = ( 9×2 = 18 ATP and 6×2= 12 NADPH2 required.)
-
Most of the
Plants are C3 plants.
However Sucrose is transported in plants as the food material.
Want to Know about Cellular Respiration:
https://uksirnotes.blogspot.com/2021/05/plant-physiology-respiration-by-uk-sir.html
Want to Know about Phyto Hormones:
***








Awesome notes sir
ReplyDelete